
When you own a share of common stock, it means you own a little part of that company. This ownership gives you the right to vote on important company decisions and sometimes get a share of the company’s profits, which are called dividends. The other main type of stock is called preferred stock and works a bit differently. The main difference is that preferred stock has a fixed, guaranteed dividend, while common stock dividends can change over time or even be discontinued. For this reason, share prices of preferred stocks generally don’t fluctuate as much as common stock. The company may occasionally issue common stock in exchange for services received or rendered.
How to Invest in Preferred Stock
No, common stock is not a real asset because its value does not come directly from its physical properties. Common stock is a financial asset because it is a non-physical contract that confers an equity ownership stake in a company. Public companies need extra cash for many purposes, including upgrading production facilities, expanding into new markets, and pursuing acquisitions. One of the easiest ways to raise funding is through issuing common stock, which comes with both advantages and disadvantages when compared to taking out a traditional loan. Assets are things that could increase the value of a company over time, while liabilities are debts that must be paid or goods and services obligations that must be fulfilled. Both common stock and preferred stock have pros and cons for investors to consider.
To Ensure One Vote Per Person, Please Include the Following Info
This shows how well management uses the equity from company investors to earn a profit. Part of the ROE ratio is the stockholders’ equity, which is the total amount of a company’s total assets and liabilities that appear on its balance sheet. Common stock includes all shares issued, including those reacquired as treasury stock. Since treasury stock is not currently owned by stockholders, it should not be included as part of their worth.
Dividends
If a company is healthy, the total assets will be larger than the total liabilities. The residual amount left to the owners is known as shareholders’ equity and is represented by a company’s shares. One of the primary reasons for calculating common stock on the balance sheet is to provide financial transparency. The balance sheet shows the company’s assets, liabilities, and equity, which helps stakeholders understand the company’s financial position. The calculation of common stock provides additional information about the company’s ownership structure and how many shares of stock are outstanding.
Investing in common stock means you’re putting your money into a part of the company’s journey. Understanding how dividends, voting rights, and the value shown in financial reports affect your investment as a stockholder can help you make smarter choices. Always remember, investing is not cash flow from assets calculator just about making money; it’s about being part of a company’s story and holding a stake as a common stockholder. The more shares of common stock you have, the bigger your part of the company. It’s a way for people to invest in a company and possibly make money if the company does well.
- When you own a share of common stock, it means you own a little part of that company.
- Common stock, as its name implies, is one of the most ordinary types of stock.
- To put it simply, it is the acquisition of funds through the sale of business ownership.
- The issuance of common stock cannot be more than the authorized number but can give less than the number of authorized shares.
- In this example, Apple’s total assets of $323.8 billion is segregated towards the top of the report.
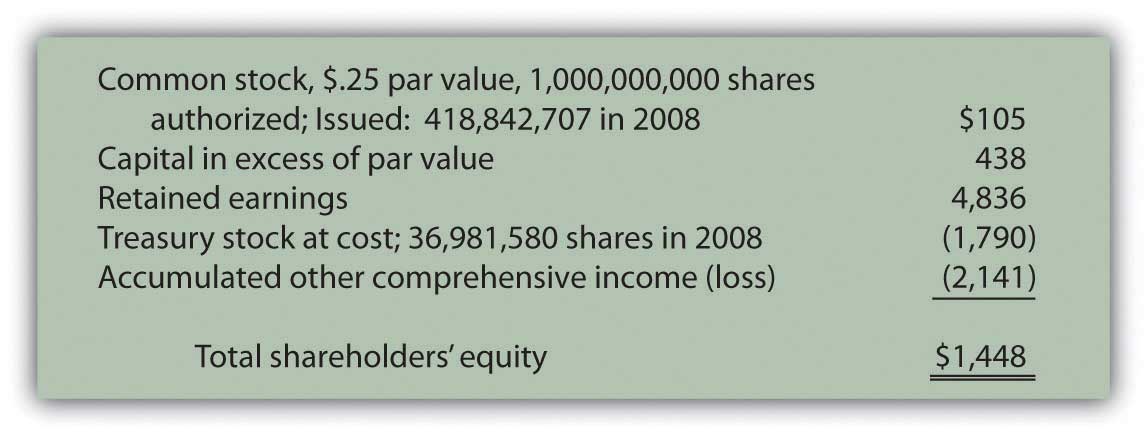
Shareholders’ equity belongs to the shareholders, whether they’re private or public owners. A company’s balance sheet is one of the most important financial statements it produces—typically on a quarterly or even monthly basis (depending on the frequency of reporting). In other words, they have a priority claim on the liquidated company’s assets. Common stockholders may run the risk of losing their entire equity in a company because they are paid out last, after bondholders and preferred stockholders.
Therefore, the company currently has authorized 5,000 shares and has 2,000 shares issued and outstanding. When people think about investing in a company, common stock is a big deal. Let’s dive into how common stock plays a huge role in making investment choices, focusing on dividends, voting rights, and its value in financial reports. Callable preferred stocks can be repurchased by the issuer at a preset date and price, causing you to miss out on future dividends. Convertible preferred stock, meanwhile, can be converted into common stock at the company’s discretion, which can be an advantage if the price of the common stock rises significantly. Companies fund their capital purchases with equity and borrowed capital.
Common and preferred stock both let investors own a stake in a business, but there are key differences that investors need to understand. Treasury shares would be deducted from total shares only when they exist. Conceptually, stockholders’ equity is useful as a means of judging the funds retained within a business. If this figure is negative, it may indicate an oncoming bankruptcy for that business, particularly if there exists a large debt liability as well.
The issue and exact figure of dividends for common stock varies and is dependent on company performance. Broadly defined, common stock can be thought of as the bedrock of a company’s public offerings. Common shares are issued without promise of dividend to individuals who are interested in partial ownership of the company in question. The balance sheet is an essential financial statement that provides insight into a company’s financial health and helps investors and analysts to make informed decisions. The common stockholder has an ownership interest in the corporation; it is not a creditor or lender.
There are a few exceptions to this rule, however, such as companies that have two classes of common stock — one voting and one non-voting. The company’s class A shareholders (GOOGL -1.33%) have voting rights, while its class C shareholders (GOOG -1.33%) do not. If a company or organization is privately held by a single owner, then shareholders’ equity will be relatively straightforward. If it’s publicly held, this calculation may become more complicated depending on the various types of stock issued.
